Not translating pages or parts of them
Sometimes you have parts of your website that you would rather not translate. For example, consider quotes, article names or other fragments of text that should remain untranslated. Also, you may not want to translate entire pages because you do not consider them important and thus want to save costs on additional character bundles.
Excluding via Clonable
Each clone is limited to a total of 20 wildcard page exclusions.
To make sure you don't have to make changes your original website, Clonable offers a way to do it through your clone's settings as well. These settings can be found under: clone > advanced settings > page exclusions.
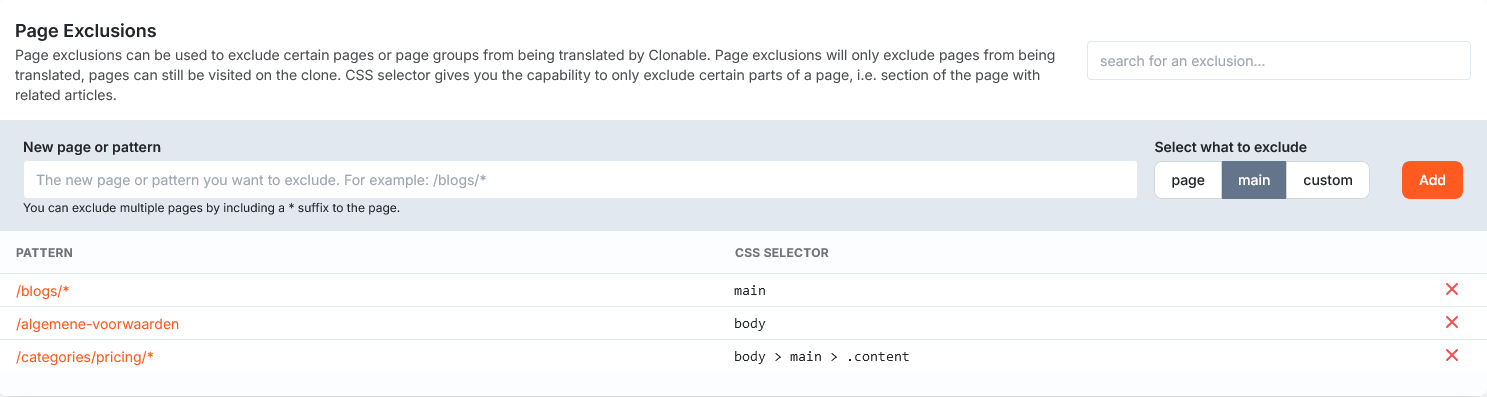
If you are going to use the translated urls from the clone, the page exclusions will not work.
Excluding entire pages
When excluding pages, you can choose to exclude a single page, or a group of pages. This allows you to exclude all blogs from translation, for example. This will ensure that the entire page (including menu and footer) will not be translated.
If you simply want to exclude a single page for translations, you can add the path to that page to the page exclusions.
Sometimes you don't just want to exclude a single page, but a whole group of pages. For this, you have the option to add a wildcard after the url. This ensures that everything that matches the first part of the path is excluded. For example, if you wanted to exclude all blogs you might have the following line: /content/blogs/*.
Excluding individual blocks
In most cases, you don't want to exclude the whole page, but specifically the content that is on the page. This would allow you to still have a translated menu and/or a translated footer, for example.
To do this, you have the option of adding a CSS selector to the path. Taking the HTML page below as an example, if you wanted to exclude all the content of the blog without excluding the menu or footer, you could use, for example, .blog-content or #content as a CSS selector.
The CSS selector can be used for single pages as well as page groups.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page title</title>
<meta name="description" content="The description of the page">
</head>
<body>
<header class="menu">
<ul class="menu-items">
<li><a href="/home">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="/pricing">Price</a></li>
<li><a href="/contact">Contact</a></li>
<ul>
</header>
<main class="blog-content" id="content">
...
</main>
<footer class="footer">
<address class="footer-address">
5421XL, Scheiweg 26 <br/>
Gemert, The Netherlands
</address>
</footer>
</body>
<html>
Excluding via the original website
All of the following actions should be taken on your original website. If you try to apply the changes to the clone with substitution rules, for example, it will not work.
Excluding entire pages
If you want to exclude whole pages you can add the meta tag below to your original website. The whole page will then not be translated. Preferably place the meta tag between the <head> </head> tags of your website, but if this is not possible you can also place it somewhere else.
<head>
...
<meta clonable-translate="no">
...
</head>
Excluding individual elements
In addition to excluding an entire page, you can also exclude blocks. This gives you more flexibility about what should and should not be translated. This way it is possible, for example, to exclude only the content on a page from being translated while your header and footer remain translated. But also small elements such as individual pieces of text can be excluded from translation this way. To work best with as many systems as possible, Clonable offers two options to exclude elements.
Option 1: exclude using a CSS class
The first and often easiest option is to add a CSS class to the element you want to exclude. To exclude an element, add the class notranslate to that element.
<div>
<div class="notranslate">
<h2>Non-translatable title</h2>
<p>Non-translatable text</p>
</div>
<p>Translatable text</p>
</div>
Option 2: exclude using an HTML attribute
The second option to exclude an element from translation is through the translate="no" attribute. Adding this attribute to an element will prevent it from being translated.
<div>
<div translate="no">
<h2>Non-translatable title</h2>
<p>Non-translatable text</p>
</div>
<p>Translatable text</p>
</div>
When you exclude an element, all underlying elements (also called child elements) are also excluded from translation.:::